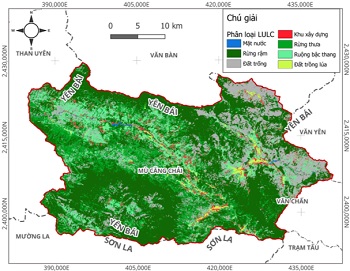
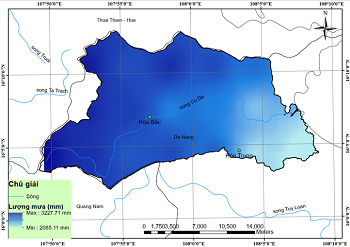
Nghiên cứu hiệu chỉnh hệ số cây trồng (C) trong dự báo xói mòn đất sử dụng cho vùng núi phía Bắc Việt Nam
16/09/2022Kết quả tính toán hệ số Ch tính toán từ các ô quan trắc với 39 lần thí nghiệm với hệ số C tra từ bảng của Hội Khoa học Đất quốc tế (HKHĐ) cho thấy có sự chênh lệch lớn, hệ số C tra từ bảng cao hơn hệ số Ch tính toán từ các ô quan trắc xói mòn từ 1,32 đến 20,0 lần, trung bình 6,07 lần. Hệ số cây trồng sau khi hiệu chỉnh bằng cách sử dụng hệ số C tra từ bảng của Hội Khoa học Đất Quốc tế nhân với trọng số phân bố lượng mưa và độ che phủ theo tháng, cần hiệu chỉnh theo hệ số các biện pháp kỹ thuật tác động vào đất, đối với các cây trồng chính các hệ số này giao động từ 0,20 đến 0,8. Kết quả sử dụng phương trình mất đất phổ dụng để kiểm định cho thấy, sử dụng hệ số hiệu chỉnh Ch cho kết quả dự báo tốt hơn so với sử dụng hệ số C tra bảng của HKHĐ.
Điều này được thể hiện qua giá trị hệ số tương quan R với đo thực tế, sử dụng hệ số C và Ch là 0,69 và 0,8 và của RMSE sử dụng hệ số C và Ch là 82,09 và 11,01.
1. ĐẶT VẤN ĐỀ
2. DỮ LIỆU VÀ PHƯƠNG PHÁP NGHIÊN CỨU
2.1. Dữ liệu
2.2. Phương pháp nghiên cứu
3. KẾT QUẢ VÀ THẢO LUẬN
3.1. Kết quả hiệu chỉnh hệ số cây trồng C
3.2. Kiểm định hệ số C hiệu chỉnh bằng mô hình USLE
4. KẾT LUẬN
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
[1] Benavidez R., B. Jackson, D. Maxwell, K. Norton (2018), "A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R)USLE): with a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates", Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 22(11), p. 6059-6086.
[2] Borrelli Pasquale, Katrin Meusburger, Cristiano Ballabio, Panos Panagos, Christine Alewell (2018), "Object-oriented soil erosion modelling: A possible paradigm shift from potential to actual risk assessments in agricultural environments", Land Degradation & Development. 29(4), p. 1270-1281.
[3] Chai T., R.R. Draxler (2014), "Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?– Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature", Geosci. Model Dev. 7, p. 1247–1250.
[4] David Wilfredo P. (1988), Soil and Water Conservation Planning: Policy Issues and Recommendations, Philippine Institute for Development Studies.
[5] Doanh L.Q., H.D. Tuan, A. Chabanne (2005), Upland Agro - Ecology Research and Development in Vietnam, Building an Agro-Ecological Network through DMC in Southeast Asia, Vientiane, Lao, p. 7.
[6] Nguyễn Văn Dũng, Trần Đức Viên và nnk (2008), "Phân tích Mức độ bền vững của hệ canh tác nương rẫy tổng hợp tại Bản Tát bằng phương pháp cân bằng dinh dưỡng", trong Trần Đức Viên, A.Terry Rambo, Nguyễn Thanh Lâm, chủ biên, Canh tác nương rẫy tổng hợp: Một góc nhìn, NXB Nông nghiệp, Hà Nội, p. 258-312.
[7] Durigon V. L., D. F. Carvalho, M. A. H. Antunes, P. T. S. Oliveira, M. M. Fernandes (2014), "NDVI time series for monitoring RUSLE cover management factor in a tropical watershed", International Journal of Remote Sensing. 35(2), p. 441-453.
[8] Nguyễn Trọng Hà (1996), Xác định các yếu tố gây xói mòn và khả năng dự báo xói mòn trên đất dốc, Trường ĐH Thủy lợi, Hà Nội.
[9] J. Brychta, Janeček M., Walmsley A. (2018), "Crop-management factor calculation using weights of spatio-temporal distribution of rainfall erosivity", Soil & Water Res. 13, p. 150-160.
[10] Kim H. S., P. Y. Julien (2006), "Soil Erosion Modeling Using RUSLE and GIS on the IMHA Watershed", Water Engineering Research. 7(1), p. 29-41.
[11] Kurosawa Kiyoshi, Nguyen Hai Do, Tat Canh Nguyen, Kazuhiko Egashira (2009), "Magnitude of Annual Soil Loss from a Hilly Cultivated Slope in Northern Vietnam and
Evaluation of Factors Controlling Water Erosion", Applied and Environmental Soil Science. 2009, p. 8.
[12] Mari Franco (2015), "The Evaluation of Soil Erosion C Factor ", International Journal of Applied Science and Technology 5(6), p. 30-38.
[13] Mepas.Pnnl.Gov 5.3.2 Soil Erodibility Factor, truy cập ngày 12/06-2018, tại trang web https://mepas.pnnl.gov/mepas/formulations/source_term/5_0/5_32/5_32.html
[14] Morgan R. P. C. (2005), Soil erosion and conservation, Third, Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
[15] Morgan Royston Philip Charles (2009), Soil erosion and conservation, John Wiley & Sons.
[16] Mulengera M. K., R.W. Payton (1999), "Estimating the USLE-soil erodibility factor in developing tropical countries", Trop Agric (Trinidad). 76(1), p. 17–22.
[17] Nguyễn Quang Mỹ (2005), Xói mòn đất hiện đại và các biện pháp phòng chống, Nhà xuất bản Ðại học Quốc Gia Hà Nội, Hà Nội.
[18] Oliveira Paulo Tarso S., Mark A. Nearing, Edson Wendland (2015), "Orders of magnitude increase in soil erosion associated with land use change from native to cultivated vegetation in a Brazilian savannah environment", Earth Surface Processes and Landforms. 40(11), p. 1524-1532.
[19] Panagos P., P. Borrelli, K. Meusburger, E. H. Van Der Zanden, J. Poesen, C. Alewell (2015), "Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale", Environ. Sci. Policy. 51, p. 23-34.
[20] Panagos Panos, Pasquale Borrelli, Katrin Meusburger, Christine Alewell, Emanuele Lugato, Luca Montanarella (2015), "Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at the European scale", Land Use Policy. 48, p. 38-50.
[21] Renard K. G. , G. R. Foster, G. A. Weesies, D. K. Mccool, D. C. Yoder (1997), Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning With the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation, U.S Government Printing Office, Washington DC.
[22] Schmidt Simon, Christine Alewell, Katrin Meusburger (2018), "Mapping spatio-temporal dynamics of the cover and management factor (C-factor) for grasslands in Switzerland", Remote Sensing of Environment. 211, p. 89-104.
[23] Nguyễn Tử Siêm, Thái Phiên (1999), Ðồi núi Việt Nam - Thoái hoá và phục hồi, Nhà xuất bản Nông nghiệp, Hà Nội, 412.
[24] Stone R.P., D. Hilborn (2000), Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), Ontario Ministry of Agriculture and Food, Agriculture and Rural Division; Factsheet.
[25] Trung Tâm Ứng Phó Biến Đổi Khí Hậu, Dữ liệu khí tượng các trạm Cò Nòi (2015, 2016, 2017); Hòa Bình (2000), Vĩnh Yên (2000, 2001, 2002), Hà Nội.
[26] Vezina Karine, Ferdinand Bonn, Pham Van Cu (2006), "Agriculturalland-use patterns and soil erosion vulnerability of watershed units in Vietnam’s northern highlands", Landscape Ecol. 21, p. 1311–1325.
[27] Trần Quốc Vinh, Đặng Hùng Võ, Đào Châu Thu (2011), "Application of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System in evaluating soil erosion. A Case study in Tam Nong district, Phu Tho province ", Jounal of Science and Development 9(5), p. 823-833.
[28] Vrieling Anton (2006), "Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment: A review", CATENA. 65(1), p. 2-18.
[29] Wischmeier W.H. , D.D. Smith (1978), Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning, Vol. Agriculture Handbook No. 537, USDA/Science and Education Administration, US. Govt. Printing Office, Washington, DC., 58.
[30] Wischmeier W.H., D.D. Smith (1981), Predicting rainfall erosion losses -a guide to conservation planning, Supplement to Agriculture Handbook No. 537. USDA, Washington DC, USA.
[31] Zhang Changshun, Gaodi Xie, Chunlan Liu, Chunxia Lu (2011), "Assessment of soil erosion under woodlands using USLE in China", Frontiers of Earth Science. 5(2), p. 150-161.
________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chi tiết bài báo xem tại đây: Nghiên cứu hiệu chỉnh hệ số cây trồng (C) trong dự báo xói mòn đất sử dụng cho vùng núi phía Bắc Việt Nam
Trần Minh Chính
Viện Khoa học Thủy lợi Việt Nam
Nguyễn Trọng Hà
Trường Đại học Thủy lợi
TẠP CHÍ KH&CN THỦY LỢI
Ý kiến góp ý: